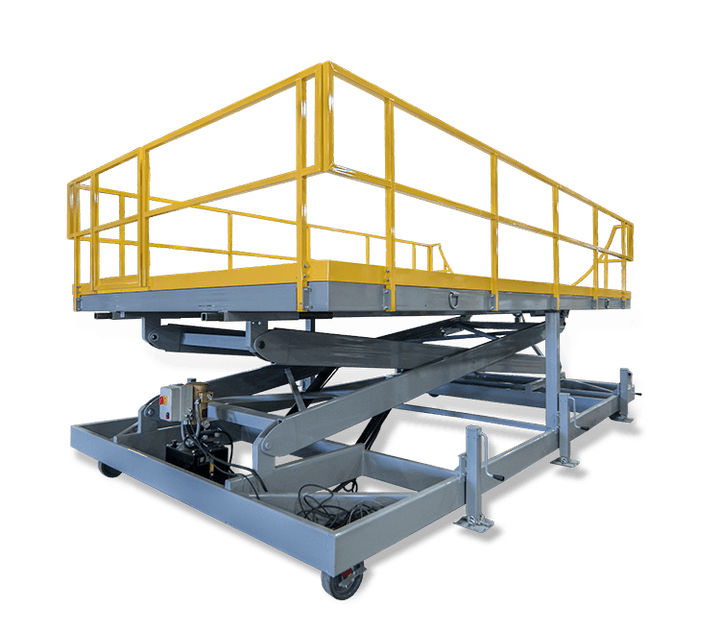
Rapid Prototyping Services
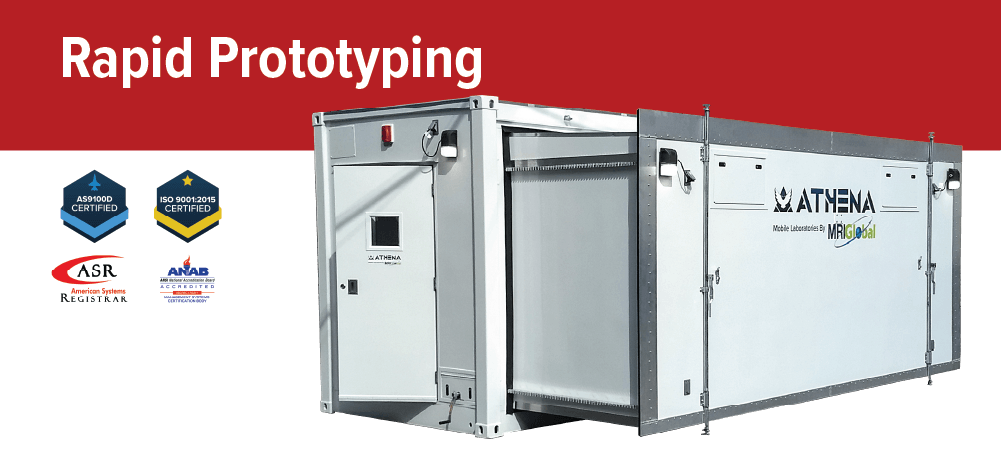
Craftsmen’s team of highly skilled industrial fabrication specialists service a wide range of custom and production rapid prototyping services for corporations and government organizations
Craftsmen Industries knows that the early stages of the development process for your products are the most important. Which is why we take pride in offering an abundance of rapid prototyping options that are sure to give your products a great head start no matter which method you may chose.
Let Craftsmen take your idea and produce a high quality prototype that will allow you to showcase your new product in confidence!
.
The Craftsmen Difference:
Design - Engineering - Fabrication
Paint - Graphics - 3D Additive Manufacturing
All Under One Roof!
Dedicated to the Highest Quality Standards
We prioritize superior quality management and are certified by ASR with the prestigious AS9100D and ISO 9001:2015 certifications.





Vision
Tell us about your idea! Describe it, sketch it, or show us your designs.

Design
We design your solution down to the last bolt.
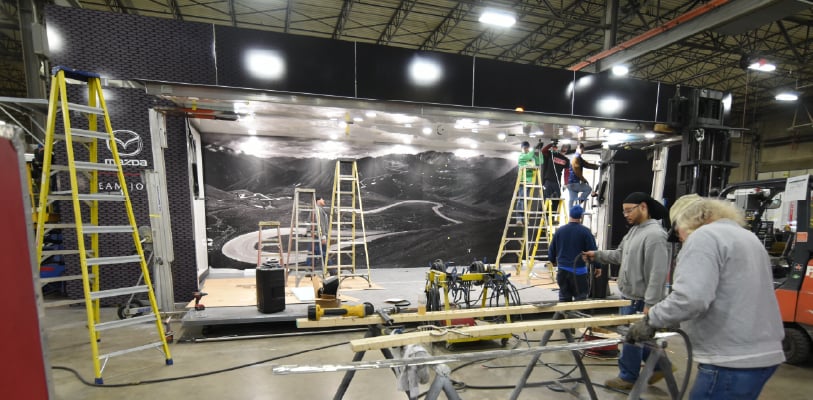

Build
We custom fabricate your build in-house.
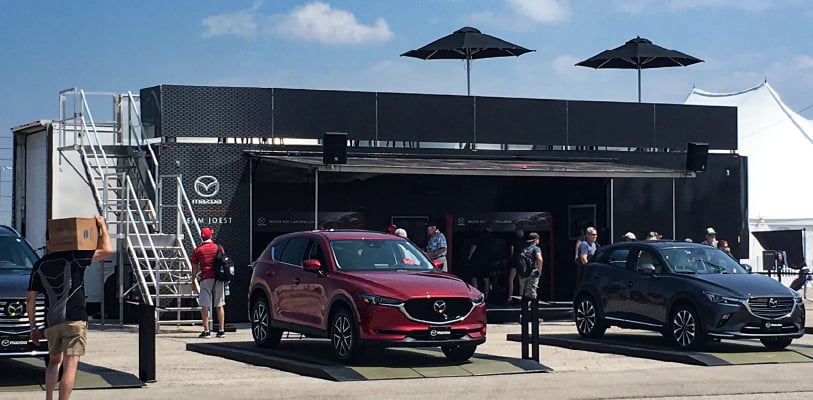

Deliver
We deliver your asset on time as promised.









































"If you want to build the impossible, Craftsmen has the tools and talent. They are more like a Venture partner than a builder."
Founder & CEO
Magicbox
Magicbox
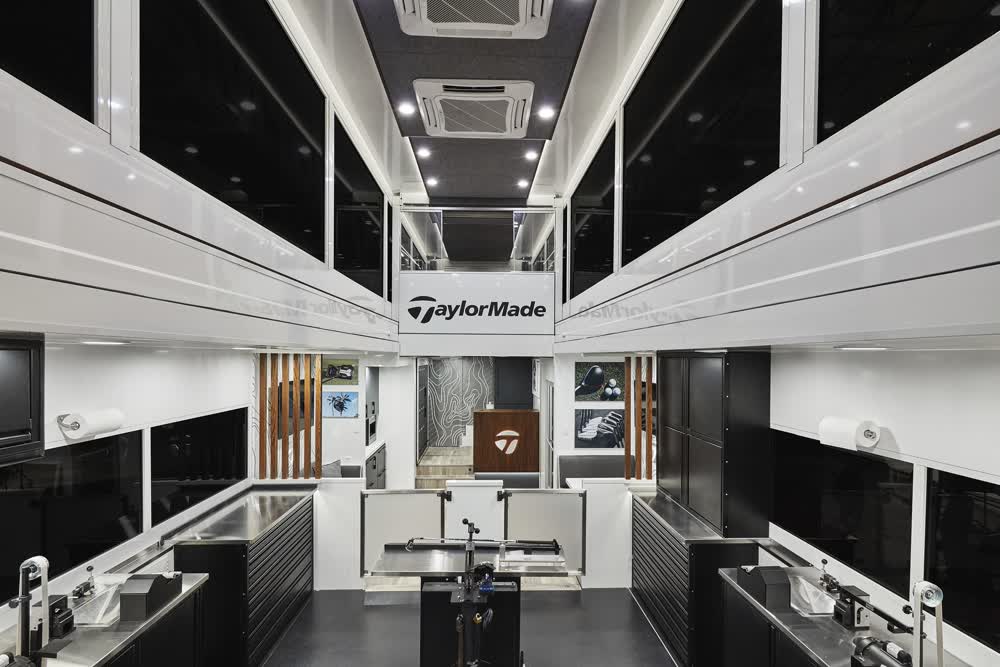

"Craftsmen, hands down, had the best ideas, best drawings. They were as passionate about the project as I was. I don't know why anyone would go anywhere else."
PGA Tour Technician
TaylorMade
TaylorMade
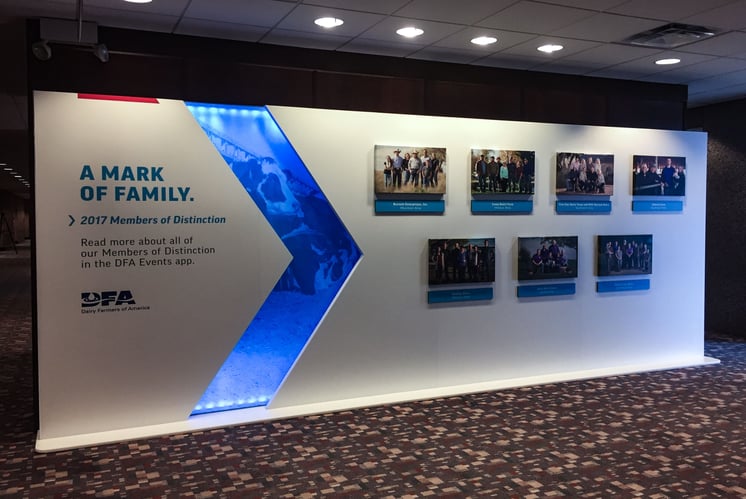

"High caliber work, great crew of talented workers who come up with creative solutions and are easy to work with, overall great partners."
Creative Director
Dairy Farmers of America
Dairy Farmers of America

"The team at Craftsmen is top notch and they always get the job done no matter the deadline. I consider them an extension of our team - a true partner!"
Executive Director
Clayco
Clayco
Contact Us
TRANSFORMING YOUR IDEAS INTO HIGH-QUALITY PROTOTYPES
At Craftsmen, we specialize in rapid prototyping with over 43 years of precision manufacturing experience. Since 1982, we’ve been helping businesses turn their concepts into high-quality prototypes quickly and efficiently. Our commitment to excellence, personalized service, and cutting-edge technology ensure each prototype meets your exact specifications.
We bring your vision to life and accelerate your path from idea to creation.
Contact us
Comprehensive Rapid Prototyping Services for All Industries
At Craftsmen, we offer a range of rapid prototyping services tailored to meet the needs of various industries. Our cutting-edge technology and expert craftsmanship allow us to deliver high-quality prototypes in a fraction of the time it traditionally takes. Whether you need a single prototype or a small batch of parts, our services are designed to accelerate your product development process while maintaining precision and durability.
CNC Machining
Our CNC machining services utilize both milling and turning techniques to create prototypes and functional parts from a wide variety of materials. From intricate designs to simple geometries, we ensure each part meets tight tolerances and exceptional quality standards. This service is ideal for producing prototypes with a high degree of accuracy and durability.
3D Printing
For more complex or custom designs, our 3D printing services offer fast turnaround times and the ability to create highly detailed prototypes with intricate geometries. We use a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and resins, to bring your designs to life quickly, whether you need a single prototype or a series of test models.
Injection Molding
If you're looking for low-volume production or rapid tooling for your prototypes, our injection molding services provide the perfect solution. We use the latest technology to produce high-quality molded parts with precise details, helping you test the fit and functionality of your design before full-scale production.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Our sheet metal fabrication capabilities include laser cutting, bending, welding, and more. This is ideal for creating functional prototypes from metals and alloys that require both strength and flexibility, allowing you to test and refine your design for real-world applications.
Custom Extrusions
For designs requiring unique shapes or profiles, our custom extrusion services deliver precise, high-quality parts in various materials such as aluminum and plastics. With custom tooling, we can produce prototypes and short-run parts that meet your specific design needs.
Ready to bring your design to life? Contact us today to learn more about how our rapid prototyping services can help you move your project forward!
Why Choose Craftsmen for Your Rapid Prototyping Needs?
When it comes to rapid prototyping, quality, speed, and precision are non-negotiable. Craftsmen has been a trusted name in the industry since 1982, offering unparalleled expertise in creating prototypes that help bring your ideas to life. Our commitment to innovation, coupled with our decades of experience, sets us apart from competitors and makes us the ideal partner for your prototyping needs.
Proven Experience
With over 40 years of experience, we understand the complexities of prototyping and product development. Our skilled team is equipped with the latest technology and an extensive knowledge base to ensure that your prototypes meet the highest standards of quality and accuracy. Whether you're a startup or an established company, we have the tools and expertise to help you succeed.
Unmatched Precision
Precision is key when it comes to prototyping, and we pride ourselves on delivering parts that meet even the most stringent tolerances. Our CNC machining and 3D printing services use state-of-the-art equipment, ensuring that each prototype we create is an accurate representation of your design, with no compromises on quality.
Fast Turnaround Times
Time is often of the essence in prototyping, and we understand the importance of meeting deadlines. Our efficient processes and advanced technologies allow us to provide rapid prototyping services with quick turnaround times, often delivering parts in just days rather than weeks. This helps you test, refine, and perfect your design without unnecessary delays.
Experience the difference of working with a company that values precision, quality, and speed.
Contact Craftsmen today and let us help you bring your prototype to life faster than ever before!
Custom Prototyping Solutions for Aerospace, Automotive, and Medical Industries
At Craftsmen, we take pride in providing rapid prototyping solutions to a wide range of industries. Our versatile capabilities allow us to support the needs of businesses in automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer electronics, and more.
Automotive
From prototype car parts to custom vehicle components, our rapid prototyping services help automotive companies accelerate product development and reduce time-to-market. Whether you're designing engine components, interior parts, or electrical systems, we have the expertise to bring your vision to life.
Aerospace
Precision is key in the aerospace industry, and at Craftsmen, we deliver prototypes that meet the highest standards. Our prototyping services support the development of everything from aircraft parts to components used in satellite systems, ensuring your parts are both reliable and durable.
Medical
In the medical field, precision, safety, and performance are paramount. We specialize in creating high-quality prototypes for medical devices, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment. Our rapid prototyping services help medical manufacturers test functionality, fit, and performance before full-scale production.
Consumer Electronics
We support the consumer electronics industry by producing prototypes for everything from smartphones to wearable technology. Our ability to quickly create and refine prototypes helps our clients reduce development time and get their products to market faster.
Explore Our Industry Solutions
No matter your industry, we have the expertise to bring your ideas to life.
Contact us to learn how we can help accelerate your product development.
Common Types of Prototyping Projects at Craftsmen
We specialize in producing a variety of custom prototypes tailored to your specific needs. Some of the most common types of prototyping projects we handle include:
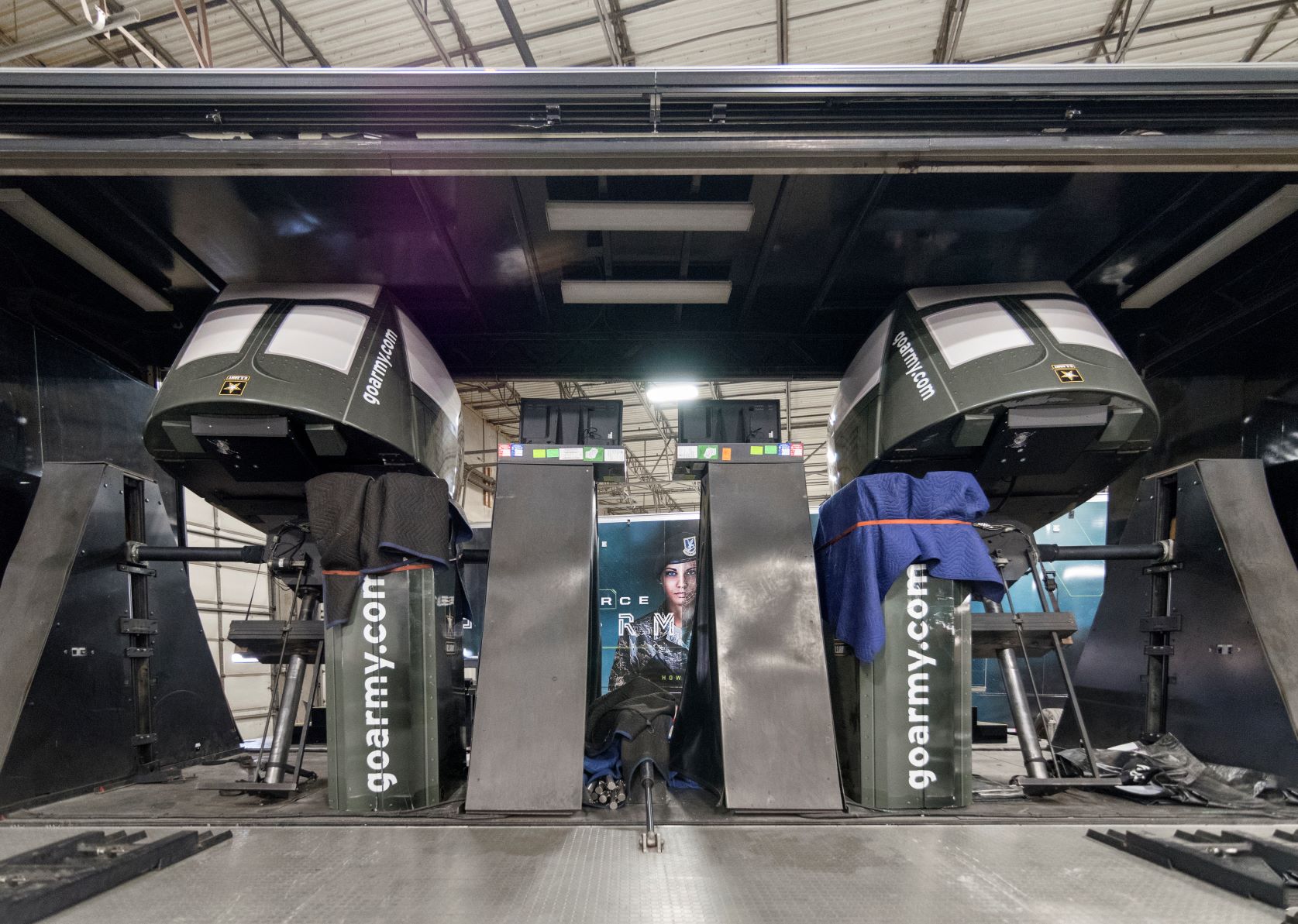
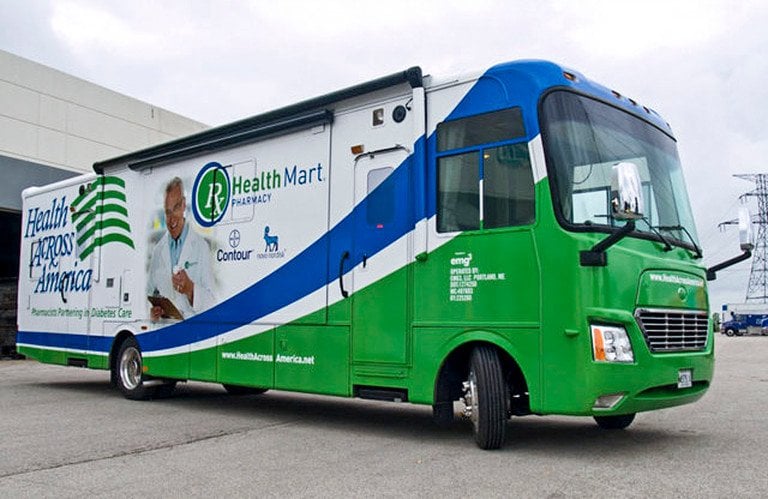
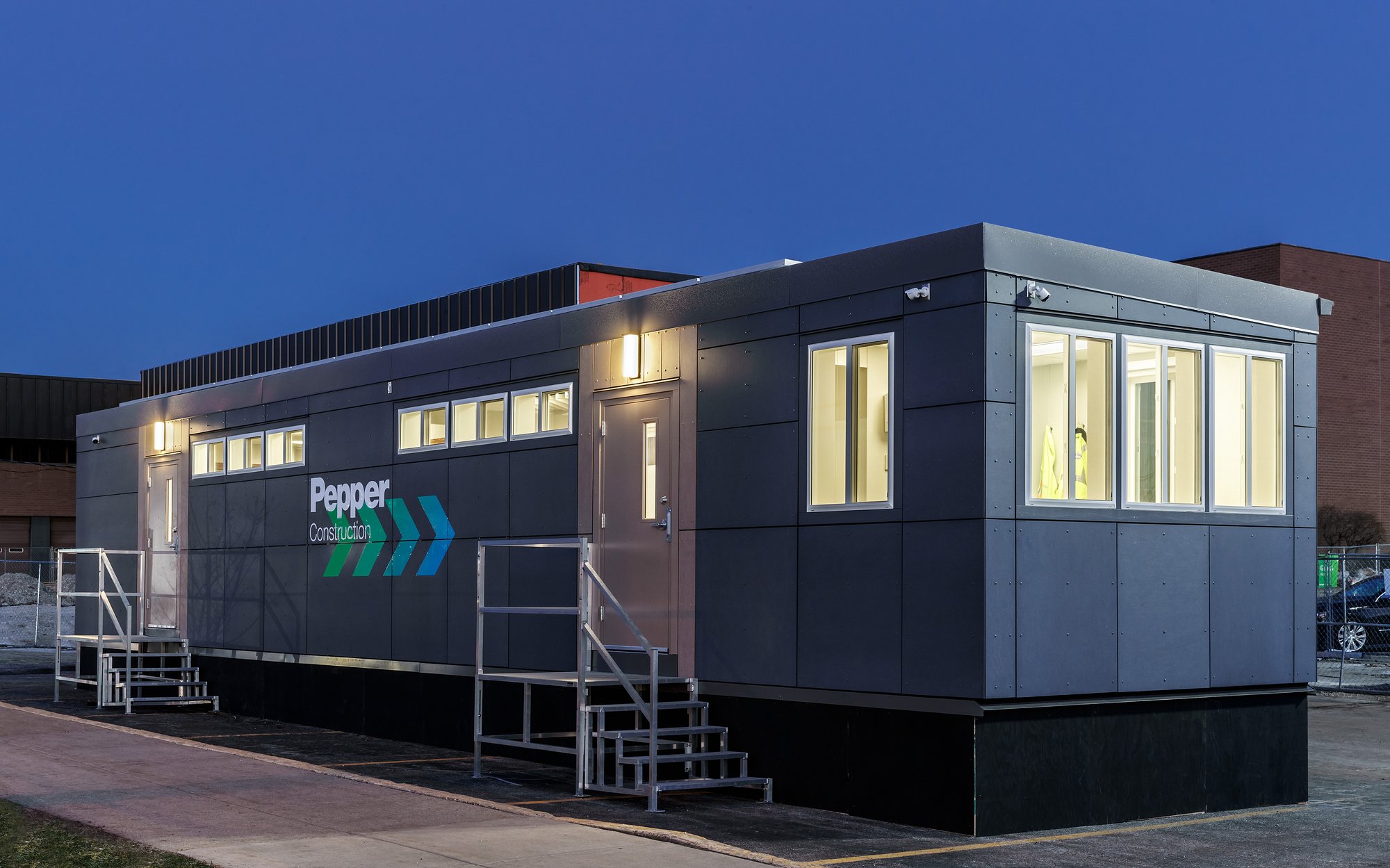
- Mobile Laboratories
- Mobile Surveillance Units
- Data Collection Units
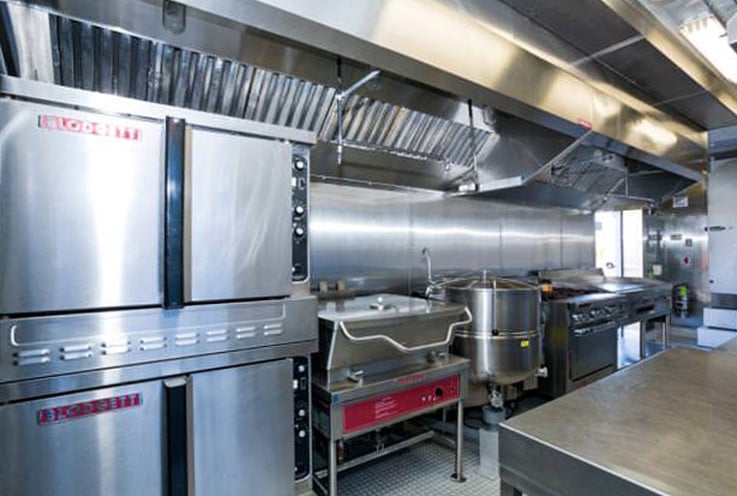
- Mobile Kitchen Units
- Battery Storage Containers
- Filtration Containers
- Water Treatment Containers
These projects often require precision, speed, and adaptability—all things Craftsmen excel at. Our team can help transform these complex ideas into tangible, fully functional prototypes, ready for testing and further development.
Common Types of Prototyping Methods We Use
To bring your designs to life, we utilize a range of advanced prototyping methods, each suited for different project requirements. These include:
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
- PolyJet
- Computer Numerically Controlled Machining (CNC)
- Injection Molding
With these technologies, we ensure that every project benefits from the most suitable method, delivering high-quality results quickly and accurately.
Materials We Use in Rapid Prototyping
At Craftsmen, we offer a broad range of materials tailored to your specific prototyping needs. Whether you're building precision parts for aerospace or robust components for automotive, our material selection is optimized for quality, durability, and performance.
- DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering): Ideal for small, high-precision parts, we use metals like stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and Inconel—perfect for parts requiring strength and heat resistance.
- MJF (Multi Jet Fusion): For lightweight, functional prototypes, we use black nylon and other versatile materials that balance performance and ease of manufacturing.
- Large-Scale Prototypes: For complex, large-scale projects such as mobile labs or surveillance units, we use heavy-duty materials like aluminum and steel to ensure structural integrity and reliability.
Choosing the right material early in the design phase helps accelerate your project, ensuring that your prototype meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Get in Touch Today to Discuss Material Options for Your Project.
Timelines for Rapid Prototyping
Time is crucial, and Craftsmen delivers rapid results that keep your project moving forward.
- Quick Turnaround: Need a prototype in a hurry? Small parts can be ready in as little as 1 day—ideal for quick tests and revisions.
- Mid-Size Prototypes: Projects requiring more detail and complexity typically take between 1 week to 1 month.
- Large-Scale Projects: For larger, intricate prototypes like mobile labs or custom surveillance units, timelines can extend to several months, ensuring precision and quality every step of the way.
The right process for your needs will determine the timeline, but no matter the size, we’re committed to delivering speed without compromising quality.
Let Us Help You Meet Your Project’s Timeline—Request a Quote Today.
Cost of Rapid Prototyping
The cost of rapid prototyping depends on several factors, but one thing is clear: we make your investment count.
- Machining Method: From CNC machining to 3D printing, the process you choose will impact the cost.
- Size & Design Complexity: Larger or more detailed designs naturally require more material and time.
- Material & Finishing: The quality of materials (like stainless steel or nylon) and post-production finishing (such as polishing or coating) can influence pricing.
- Post-Production Evaluation: Extensive testing or revisions could increase the overall cost.
Ready to Get Started? We offer competitive pricing tailored to your unique project needs.
The Process: From Concept to Completion
At Craftsmen, we make the prototyping process straightforward, ensuring a smooth journey from initial concept to finished product. Our step-by-step approach ensures transparency, quality, and speed at every stage.
- Step 1: CAD File Submission
Submit your CAD files directly to us. Whether it's a detailed design or a rough concept, our team will ensure it's ready for the next steps. - Step 2: Quoting & DFM Feedback
Once we receive your CAD files, we provide a fast and accurate quote. Additionally, we offer Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback to ensure that your design is optimized for cost-effectiveness and manufacturability. - Step 3: Production
Once the design is finalized, our experienced engineers begin the production process. We use cutting-edge technologies like CNC machining, 3D printing, and injection molding to create your prototype to precise specifications. - Step 4: Shipping
After production, we ensure that your prototypes are packaged and shipped quickly, meeting your deadlines. We offer expedited shipping options for those critical time-sensitive projects.
Start Your Project with Us
Ready to bring your ideas to life?
Start your prototyping journey with us today by submitting your CAD files for a quick quote.
Fast Turnaround & Lead Times
Speed is crucial when it comes to prototyping, and at Craftsmen, we understand the importance of quick lead times. Whether you're looking for a one-off prototype or a batch of parts, we can deliver faster than traditional manufacturing methods.
Quick Lead Times
Our rapid prototyping services guarantee fast turnaround times, often delivering prototypes in just a few days. We understand the need to test and iterate quickly, and we deliver without compromising on quality.
Expedited Services
In urgent cases, we offer expedited services to ensure your prototypes are ready in record time. Whether you need a prototype for testing, demonstration, or validation, our team will work diligently to meet your deadlines.
Get Your Parts Fast
Request a Quote Today
Don't let time slow you down.
Reach out now for a fast, reliable quote and get your prototypes delivered quickly.
Engineering & Design Support
At Craftsmen, we don’t just stop at producing prototypes—we offer comprehensive engineering and design support to ensure your project is a success. Our team of experts is here to guide you at every stage of the design and manufacturing process.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Feedback
We provide valuable DFM feedback, helping you optimize your design for cost-effectiveness and manufacturability. This step ensures that your prototype can be produced efficiently without compromising quality.
Live Consultations & Support
If you have questions or need expert advice, our engineers are available for live consultations. We’re here to help you refine your designs and tackle any challenges that arise during the prototyping process.
Speak to an Engineer Today
Need expert guidance on your design?
Contact our engineering team today for personalized support.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
How much does rapid prototyping cost?
The cost of rapid prototyping varies based on design complexity, materials, and manufacturing method. Prices typically range from $50 to $5,000+, with simpler parts being more affordable. Complex prototypes with specialized materials may cost more. Request a custom quote for a more accurate estimate.
- How long does rapid prototyping take?
The timeline for rapid prototyping varies depending on the complexity of the project. Simple prototypes can often be produced in 1-3 days, while more intricate designs may take 1-4 weeks to complete. The process can be expedited for urgent projects, with some services offering expedited options to meet tight deadlines.
- What types of industries use rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is used across a wide range of industries including automotive, aerospace, medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. Businesses in these sectors rely on rapid prototyping to test designs, improve functionality, and reduce time-to-market for new products.
- Can rapid prototyping help reduce product development time?
Yes! One of the main benefits of rapid prototyping is its ability to significantly shorten product development timelines. By quickly creating prototypes, you can test and refine designs, identify potential issues early on, and make necessary changes before committing to full-scale production. This helps speed up the overall development process and brings products to market faster.
- What materials can be used for rapid prototyping?
Various materials can be used for rapid prototyping, depending on the method and purpose of the prototype. Common materials include plastics (ABS, PLA), metals (stainless steel, aluminum), rubbers, resins, and composites. The choice of material impacts the prototype's strength, durability, and appearance, so it's important to select the right one based on your needs.
- Do I need a CAD file for rapid prototyping?
Yes, most rapid prototyping services require a CAD file (Computer-Aided Design) to create the prototype. CAD files provide precise dimensions and design details needed for accurate and efficient manufacturing. If you don’t have a CAD file, many prototyping companies offer design services to help create one.