Design and Materials for Mobile Medical Vehicle Interiors
Mobile medical vehicles are more than just transport; they’re fully functional healthcare spaces on wheels. The interior design and choice of...
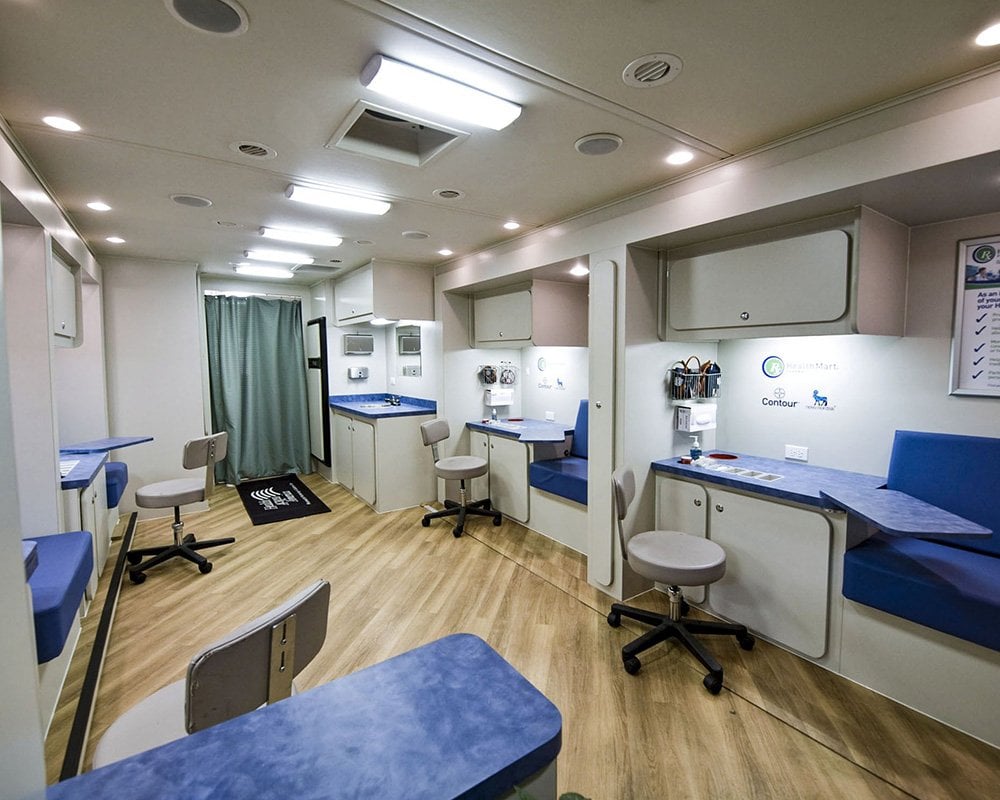
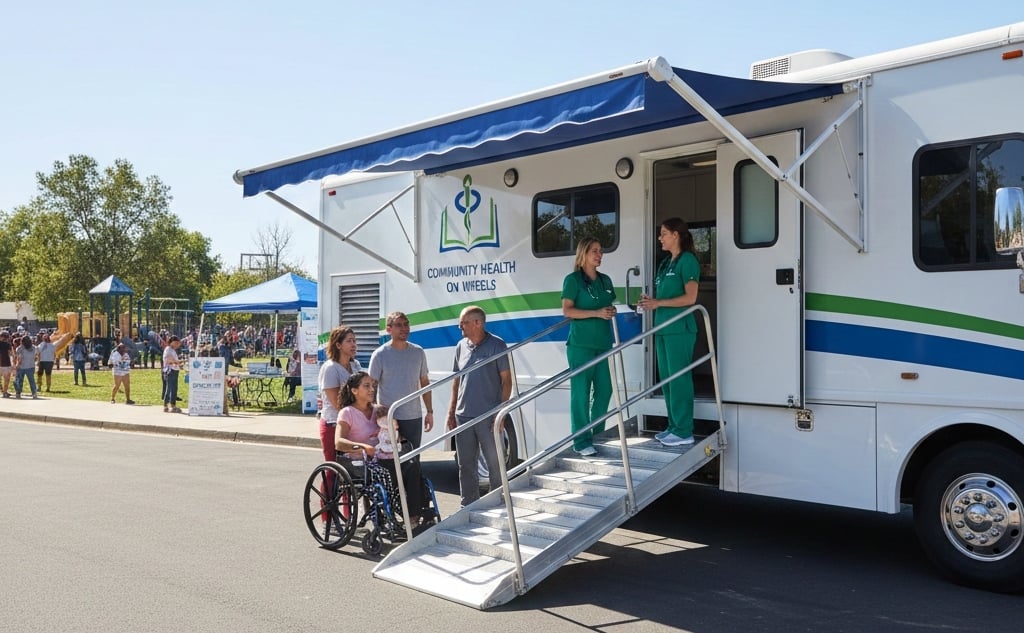
Picture a clinic with wheels, humming softly as it winds through city streets and rural roads, carrying care to those who need it most. Mobile medical clinics are more than vehicles; they are lifelines, bringing vital health services to doorsteps where hospitals feel out of reach. They represent access, immediacy, and hope wrapped into one moving solution.
What makes this possible is not just medical expertise or equipment; it is also the dedication of the medical staff. It's the behind-the-scenes systems that protect both people and tools. At the heart of it all sits the HVAC system, which controls airflow, regulates temperature, and ensures cleanliness in every square foot of the space.
This blog outlines the HVAC design standards that keep mobile clinics safe, efficient, and ready to deliver care anywhere.
In mobile health and wellness units, HVAC systems are essential for maintaining cleanliness, comfort, and compliance with healthcare standards. In mobile clinics, their role becomes even more crucial due to the confined space, fluctuating site conditions, and the need for portable power sources.
Mobile medical vehicles often operate in extreme weather conditions and rely on limited energy sources, making compact, efficient HVAC design a priority.
Mobile healthcare units must adhere to both general healthcare facility standards and specialized guidelines for mobile units. The following codes and standards provide the foundation for compliant HVAC systems:
The International Mechanical Code sets minimum requirements for the safety, installation, and performance of HVAC systems in mobile clinics.
Defines ventilation requirements, including air changes per hour, air filtration, and indoor air quality. Outpatient clinic requirements typically apply, though higher standards may be needed.
NFPA 99 Health Care Facilities Codefocuses on the safe delivery of medical gases and associated HVAC demands, particularly in clinics performing procedures.
Outlines three classification levels for mobile clinics:
Specific locations may impose additional HVAC design rules. For instance, Hanford's TFC-ENG-STD-07 addresses local hazards, such as seismic activity or dust.
Understanding FGI classifications is essential for selecting the right HVAC design. For mobile primary care clinic vehicles, choosing an HVAC design that aligns with Class 1 or 2 requirements is key to performance and compliance.
Designing HVAC for mobile settings means overcoming tight spaces, mobility, and energy limitations.
To meet code and performance needs, mobile clinic HVAC designs should incorporate:
Proper sizing of HVAC systems depends on accurate heat load estimates:
Applying these best practices ensures optimal performance and extended system life:
|
Class |
Services |
Ventilation Requirements |
Temperature Control |
Key Features |
|
Class 1 |
Imaging, diagnostics |
ASHRAE 170 outpatient + HEPA |
68°F–78°F |
Basic ventilation, energy efficiency |
|
Class 2 |
Minor procedures |
Full ASHRAE 170 + enhanced filters |
68°F–78°F |
Zoned control, optional negative pressure |
|
Class 3 |
Invasive procedures/surgery |
Fixed facility standards |
68°F–78°F |
High air changes, isolation capabilities |
Mobile clinics operate in compact, variable conditions where temperature control, air quality, and infection prevention are critical. A tailored HVAC system ensures clinical stability, safeguards equipment, and complies with healthcare standards. Off-the-shelf units simply can't meet these demands.
ASHRAE 170, the International Mechanical Code, and NFPA 99 set the baseline for ventilation, safety, and medical gas integration. The Facility Guidelines Institute (FGI) further refines requirements by clinic classification, defining filtration levels, airflow rates, and zoning protocols based on clinical use.
FGI Class 1 clinics, used for diagnostics, require basic ventilation. Class 2, which supports minor procedures, requires improved filtration and airflow control. Class 3 clinics, equipped for invasive care, must mirror hospital-grade standards with precise temperature, pressure, and filtration metrics.
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, directional airflow, and zoned pressure areas reduce contamination risks. Negative-pressure isolation, when necessary, prevents the spread of aerosols. Regular maintenance, including filter changes and airflow checks, helps keep the system clinically safe.
Energy-efficient HVAC units minimize strain on onboard generators. Dual-power systems allow switching between internal and shore power. Solar or battery backups extend uptime, ensuring uninterrupted climate control even during transport or grid loss.
Mobile HVAC systems are exposed to vibration, dust, and extreme weather conditions. Reinforced mounts, sealed ducts, and corrosion-resistant parts are essential. Preventive maintenance, scheduled during clinic downtime, preserves performance, prolongs service life, and maintains regulatory compliance.
Designing HVAC systems for mobile clinics means more than meeting technical requirements. It requires meticulous planning, reliable engineering, and a profound sense of responsibility for patient care. From airflow regulation to energy efficiency and infection control, each element plays a critical role. When teams follow standards like ASHRAE 170 and the International Mechanical Code, they build not only compliance but also confidence. A well-designed system protects equipment, supports staff, and enables patients to receive care in a safe and stable environment, regardless of the challenges ahead.
Suppose you're ready to build a mobile clinic that delivers comfort, safety, and performance in every setting. Partner with Craftsmen Industries. Our experts design and build custom mobile medical vehicles with durable HVAC systems that support your mission and your mobility. Visit CraftsmenInd.com to get started.
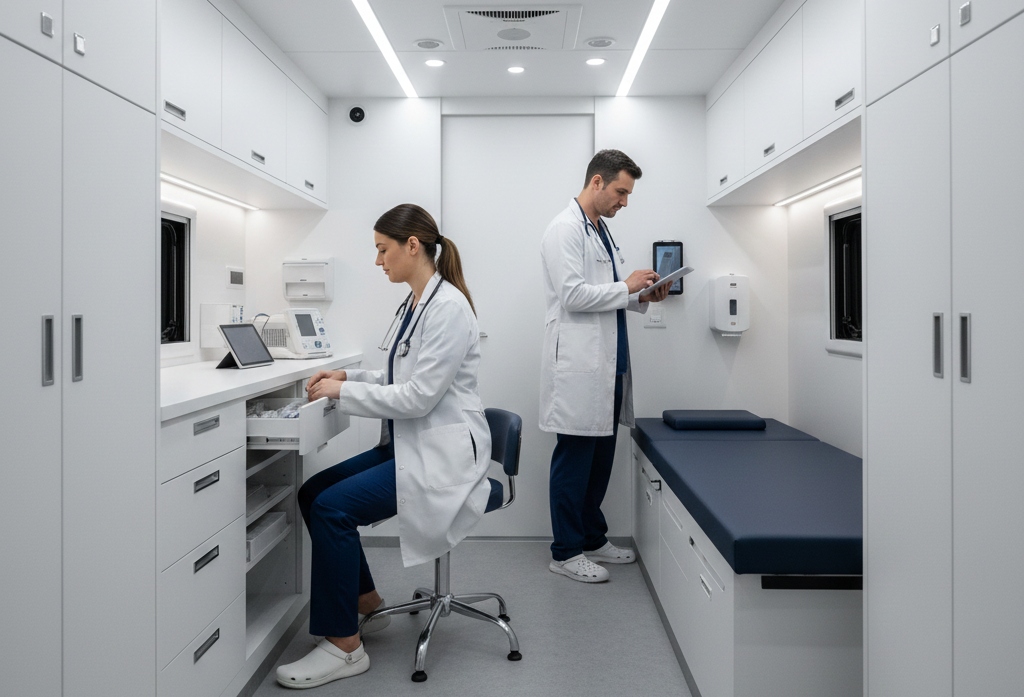

Mobile medical vehicles are more than just transport; they’re fully functional healthcare spaces on wheels. The interior design and choice of...
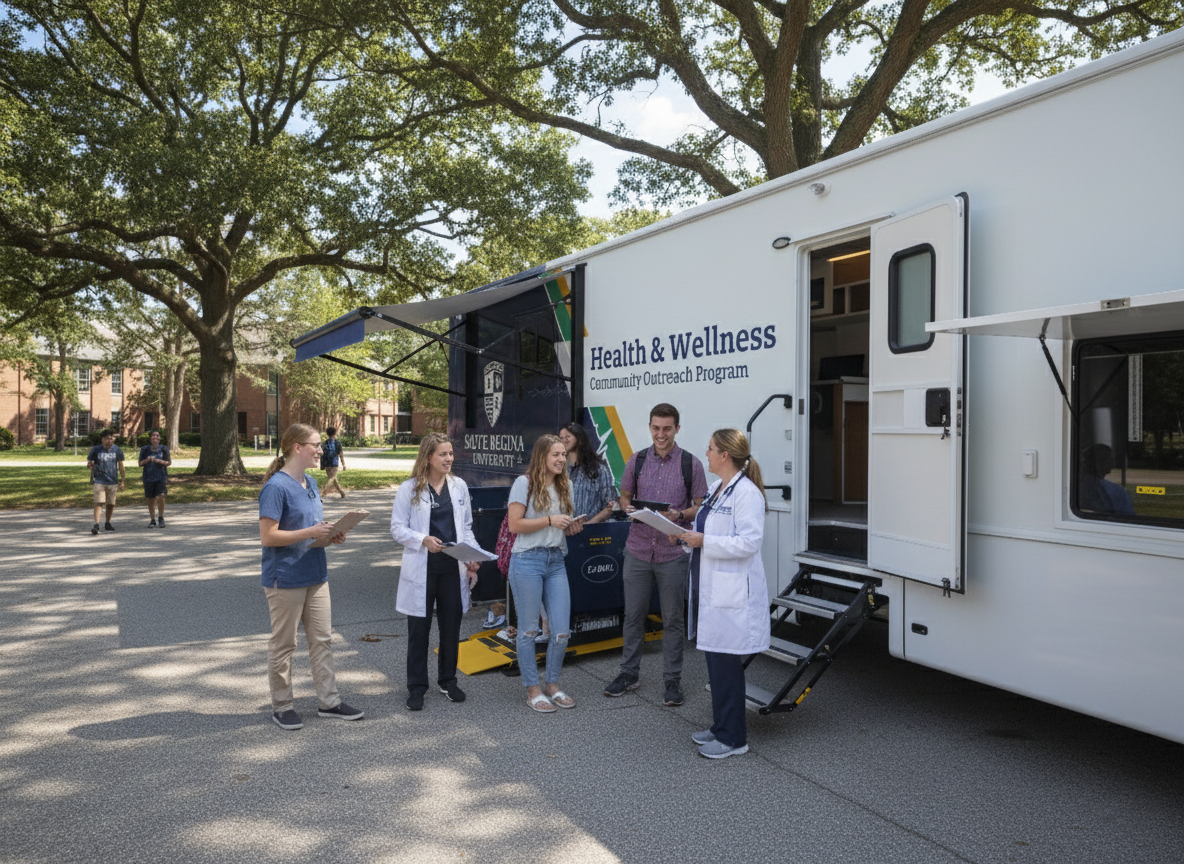

Designing a mobile medical vehicle extends beyond simply converting a trailer or RV into a clinic; it involves engineering a space that delivers...
Designing a mobile medical vehicle isn’t just about putting hospital tools on wheels; it’s about creating a self-contained, efficient care unit that...